Coffee is more popular than ever which means an increased focus on consumer satisfaction and the quality of beans via the cupping test.
The cupping test is one of the most effective methods in quality control for ensuring the product is up to scratch.Cupping coffee is important as the product has become one of the most desired drinks in the world.
The quality of a cup of coffee mainly depends on the raw material green beans from the origins and how to evaluate the quality of their sources. The cupping test method is the go-to approach for an effective valuation and here’s why.
Sense and purpose of cupping test
Below are a few reasons why the cupping test is so effective in assessing the quality of coffee beans:
- It’s a method of sensory evaluation
- It’s a quick method to determine the facts of coffee valuation
- It’s the most important step for evaluating the level of appetite and consumer satisfaction
- It depends on subjectiveness and not internationalised terminology.
- It always aligns with commercial activities
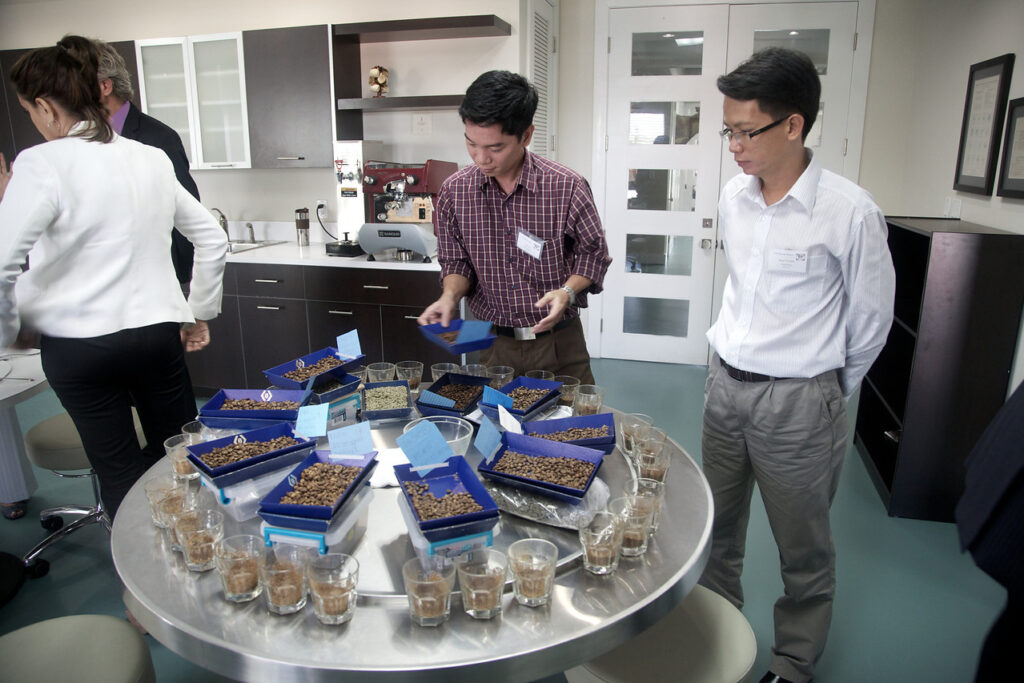

There are so many requirements to carry out when completing a cupping test. However, here are some basic requirements:
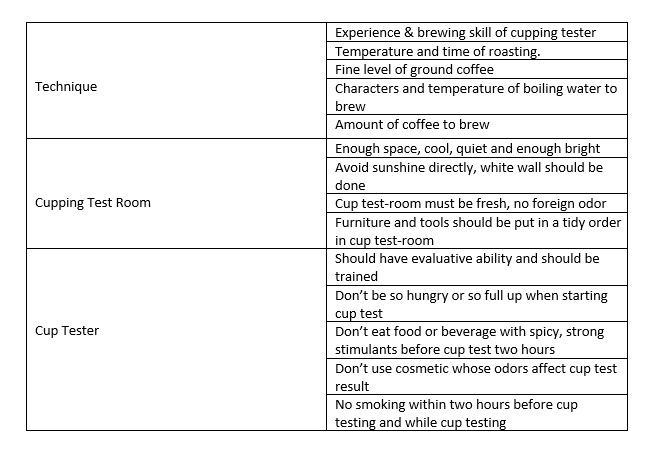

In order to carry out the process of a cupping test, some basic tools and equipment are needed. These include:
- Roaster: temperature is adjustable
- Grinder: fine level is adjustable
- Trays
- Professional spoon, volume about 10ml
- Cups with volume between 220-250ml
- Kettle to boil water
- Cupping table
- Spittoons

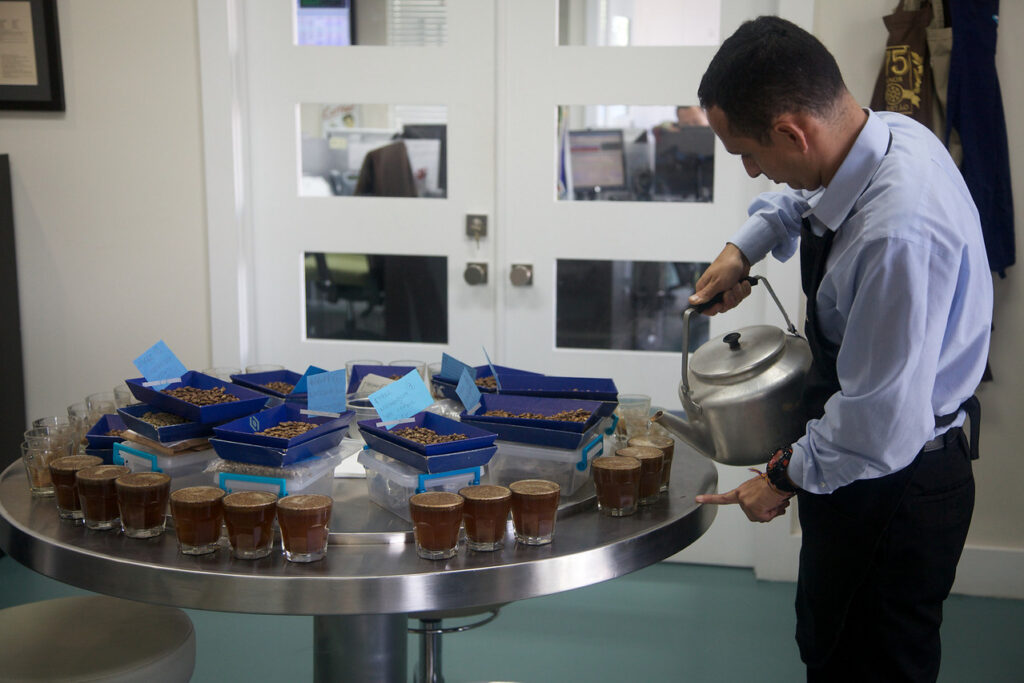
Before carrying out a cupping test, raw beans must be roasted with a basic roasting technique as below:
- Start roaster 20 minutes before
- Temperature should reach 200 degree before coffee is added
- Roasting time from is between 5-10 minutes
- End of first cracking to first of second cracking, the coffee should be taken coffee out

When finishing the roasting, we start the cupping test process:
- Roasting: 125-150gr; temperature @180oC
- Brewing ratio: 1/20 (powder/boiled water).
- Number of cups per one sample batch: 5-10 cups/ 1 sample batch; 10gr powder per cup
- Grinding: Fine level about 70% on sieve 0.6mm
- Water to brew: Fresh, no strange smells or tastes
- Don’t use hard water, distilled water, de-ionized water
- Temp. of boiled water to brew must be 98oC
- Brewing
- 200ml boiling water/cup
- Wait 2-3 minutes before soaking powder, then stirring
- After that, let skim the foam
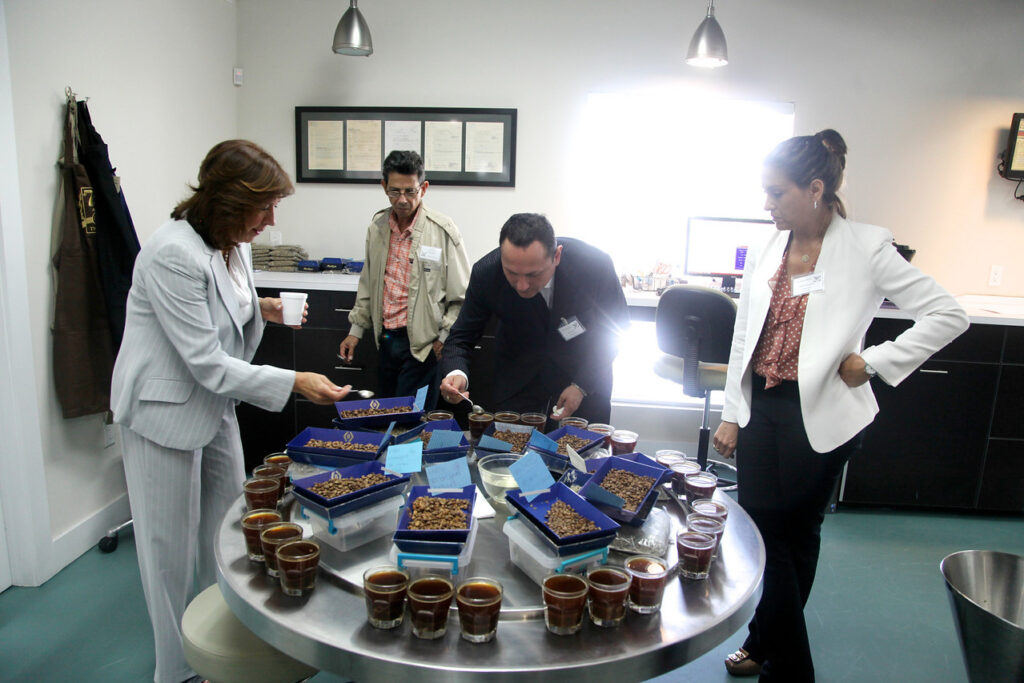
- The way how to cupping test
- Sniffing coffee brew while it is still hot
- Cupping at the temperature of brew about 50-55oC
- Use spoon to get the brew to about 6-8ml, then slurp it strongly in order to stretch the brew regularly on the surface of your tongue
- Keep it in your mouth about 3-5 seconds. Push the air from mouth to nose to feel the flavour
- Spit it into spittoon
- Should rinse spoon in fresh water regularly after cupping
- Should rinse your mouth in fresh water after cupping each sample, or eating bread to rinse your mouth if needed
- Should take a rest after 15 minutes of continuous cupping
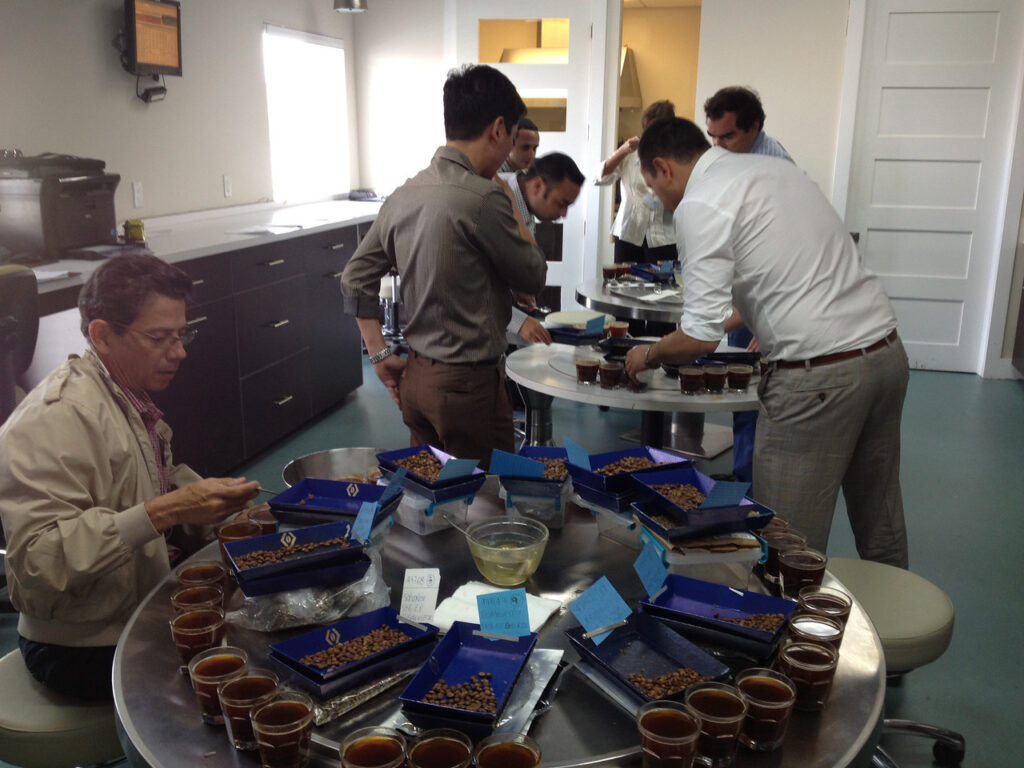

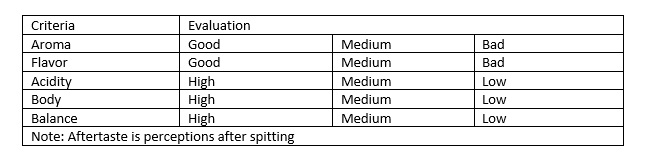
After the cupping process, the cupping tester will make the evaluation for each criteria:
There are so many defects, and we divide into four groups:
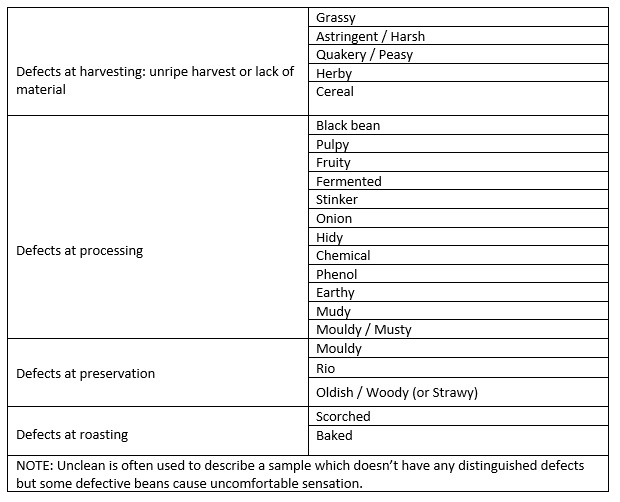
When finishing all of the above necessary steps, the cupping tester will make a cupping Test Report to submit to the relevant parties before shipment. Depending on the Report’s findings, a decision will be made about whether the shipment should be loaded or not following the terms and conditions of signing the contract. And that’s how a cupping test for coffee is carried out in quality control.
About HQTS
With over 25 years of experience in quality assurance, HQTS is ready to help your import and export business build a robust quality assurance plan. Our many service locations are prepared to be your one-stop-shop for inspection needs. Including, production monitoring, pre-shipment and sorting inspections and everything in between. Contact us today to find out how we can help you navigate your current quality control challenges.